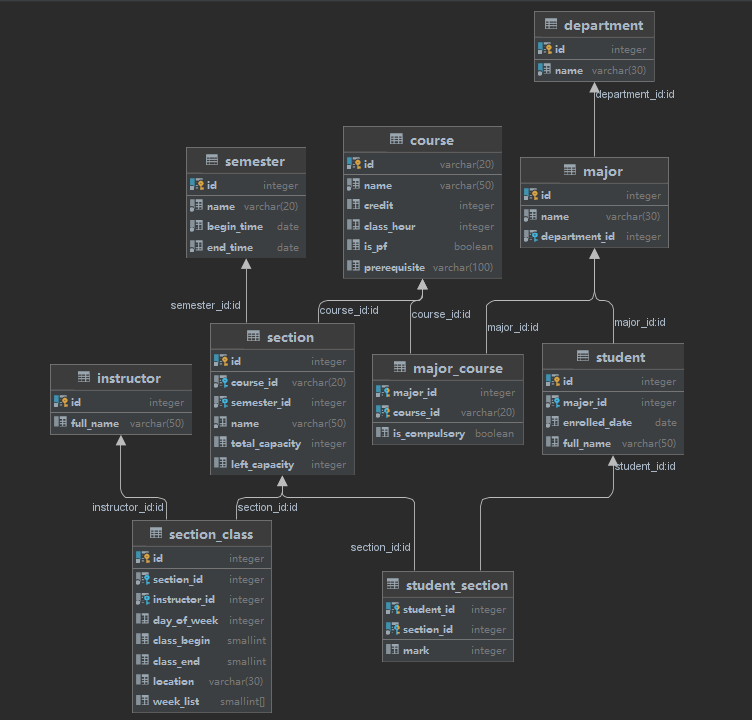
表格结构及设计 结构 共建立了10张表,其中department,major,student,course,section,section_class,instructor,semester均为储存数据的单表,major_course,student_section是多对多的关系表。
设计 系统主要分为两部分,一部分主体为课程,另一部分主体为同学,两部分与其基本信息共同构成整个关系库。表格依据需要实现接口原则,基本复原dto文件夹中的class,其中CourseSearchEntry,CourseTable为查询更新操作,不建表。User对应instructor和student两部分。基本将每个class中的成员变量转化为列储存,部分引用类型成员变量需要转化储存为基本类型。如下:
对于连接两张表关系的变量,如student.class中Major major变量,直接用major.id储存。
将prerequisite 转换为Varchar类型, 其中AndPrerequisite类型,用AND连接,OrPrerequisite类型,用OR连接,转化为如图形式,方便后续运用逆波兰算法判断是否满足先修课,若无则为null。
student_section表中,为方便储存判断,将分数course grading转化为了int类型。转化遵循逻辑如下:如果该同学本门课还没有成绩,存mark=-1,若已经登过分,百分制对应0—100;二进制分数,PASS对应-2,FAILE对应-3。
实现插入和查询 均采用demo中给的实例,写出所需sql,运用Preparedstatement插入所需元素,运用execute()执行。
优化:1、速度:给定一个成员变量connect用于连接数据库,从连接池中调用,不需要执行每个木块重新 连接,速度大大提升。
2、由于每个模块有大量重复语句,采用Util封装,可大大缩短代码量。Util 分为更新和查询两部分
update
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public static int update (Connection con,String sql,Object... param) throws SQLException{ PreparedStatement ps; try { ps = con.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 0 ; i < param.length; i++) { ps.setObject(i + 1 , param[i]); } } catch (SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(1 ); return -1 ; } return ps.executeUpdate(); } public static int addAndGetKey (Connection con,String sql,Object... param) { try (PreparedStatement ps=con.prepareStatement(sql,PreparedStatement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS)){ for (int i = 0 ; i < param.length; i++) { ps.setObject(i+1 ,param[i]); } try { ps.executeUpdate(); }catch (SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); throw new IntegrityViolationException (); } ResultSet rs = ps.getGeneratedKeys(); rs.next(); return ps.getGeneratedKeys().getInt("id" ); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(1 ); return -1 ; } }
query
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 public static <T> ArrayList<T> query (Class<T> clazz,Connection con,String sql,Object... param) { try (PreparedStatement ps=con.prepareStatement(sql)){ for (int i = 0 ; i < param.length; i++) { ps.setObject(i+1 ,param[i]); } ResultSet rs=ps.executeQuery(); ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData(); int col = rsmd.getColumnCount(); ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList <>(); while (rs.next()){ T t = clazz.newInstance(); for (int i = 0 ; i < col; i++) { Object val; String otherName = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i+1 ); switch (otherName) { case "weekList" -> val = new HashSet <>(List.of((Short[]) rs.getArray(i + 1 ).getArray())); case "dayOfWeek" -> val = DayOfWeek.of(rs.getInt(i + 1 )); case "grading" -> val = (rs.getBoolean(i + 1 ) ? Course.CourseGrading.PASS_OR_FAIL : Course.CourseGrading.HUNDRED_MARK_SCORE); case "classBegin" , "classEnd" -> val = rs.getShort(i + 1 ); case "instructor" -> { sql = """ select id, full_name "fullName" from instructor where id=?""" ; val = query(Instructor.class, con, sql, rs.getInt(i + 1 )).get(0 ); } case "student" -> { sql = """ select id, full_name "fullName", enrolled_date "enrolledDate", major_id "majorId" from student where id=?;""" ; val = query(Student.class, con, sql, rs.getInt(i + 1 )).get(0 ); } case "major" -> { sql = """ select id, name, department_id "departmentId" from major where id=?;""" ; val = query(Major.class, con, sql, rs.getInt(i + 1 )).get(0 ); } case "department" -> { sql = """ select * from department where id=?;""" ; val = query(Department.class, con, sql, rs.getInt(i + 1 )).get(0 ); } default -> val = rs.getObject(i + 1 ); } String fieldName = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i+1 ); Field field = clazz.getField(fieldName); field.set(t,val); } list.add(t); } return list; } catch (NoSuchFieldException|InstantiationException|IllegalAccessException|SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(1 ); return null ; } } public static <T> ArrayList<T> querySingle (Connection con,String sql,Object... param) { try (PreparedStatement ps=con.prepareStatement(sql)){ for (int i = 0 ; i < param.length; i++) { ps.setObject(i+1 ,param[i]); } ResultSet rs=ps.executeQuery(); ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData(); ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList <>(); while (rs.next()) { Object val; if (rsmd.getColumnName(1 ).equals("day_of_week" )) { val = DayOfWeek.of(rs.getInt(1 )); } else { val = rs.getObject(1 ); } list.add((T)val); } return list; }catch (SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(1 ); return null ; } }
Util 封装仅适用于返回数据库中建的表中列一一对应的情况,所以对于已经修改了class中成员变量从引用类型到基础类型的情况,Util中对这些特殊情况做了讨论并还原,增强了此封装的通用性。
实现接口时应用Util示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public List<Course> getAllCourses () { try (Connection con=SQLDataSource.getInstance().getSQLConnection()){ String sql= """ select id, name, credit, class_hour "classHour", is_pf grading from course;""" ; return Util.query(Course.class,con,sql); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(1 ); return null ; } }
add
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public int addCourseSection (String courseId, int semesterId, String sectionName, int totalCapacity) { try (Connection con=SQLDataSource.getInstance().getSQLConnection()){ String sql="insert into section (course_id,semester_id,name,total_capacity,left_capacity) values (?,?,?,?,?)" ; return Util.addAndGetKey(con,sql, courseId, semesterId, sectionName, totalCapacity, totalCapacity); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(1 ); return -1 ; } }
性能 & 性能分析 Resource Consumption
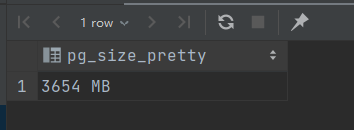
Memory Consumption:
1 select pg_size_pretty(pg_tablespace_size('pg_default' ));
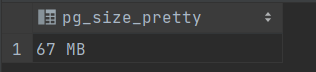
Disk Consumption
数据库
1 select pg_size_pretty(pg_database_size('project_class2' ));
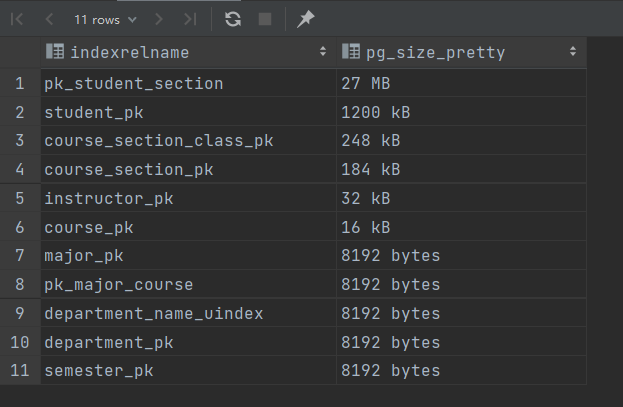
索引
1 select indexrelname, pg_size_pretty(pg_relation_size(relid)) from pg_stat_user_indexes where schemaname= 'public' order by pg_relation_size(relid) desc ;
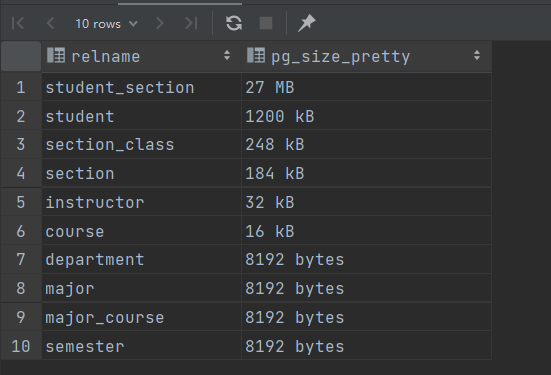
表本身(不含索引)
1 2 select relname, pg_size_pretty(pg_relation_size(relid)) from pg_stat_user_tables where schemaname= 'public' order by pg_relation_size(relid) desc ;
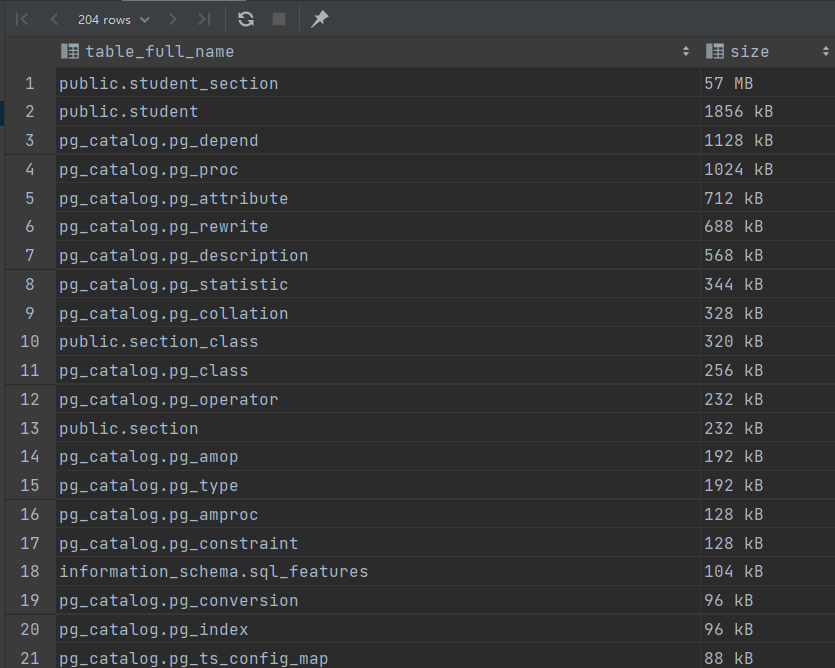
表包括索引所占内存:
1 2 3 4 5 6 SELECT table_schema || '.' || table_name AS table_full_name, pg_size_pretty(pg_total_relation_size('"' || table_schema || '"."' || table_name || '"' )) AS size FROM project_class2.information_schema.tablesORDER BY pg_total_relation_size('"' || table_schema || '"."' || table_name || '"' ) DESC
上述搜索结果可得,索引和数据占据内存相近,他们构成了整个数据库的大部分内存,还有一些内存用于储存pg_和information_表格,占一小部分。其中,占内存最大的是student_section表格(57/67),它的数据接近五十万条。
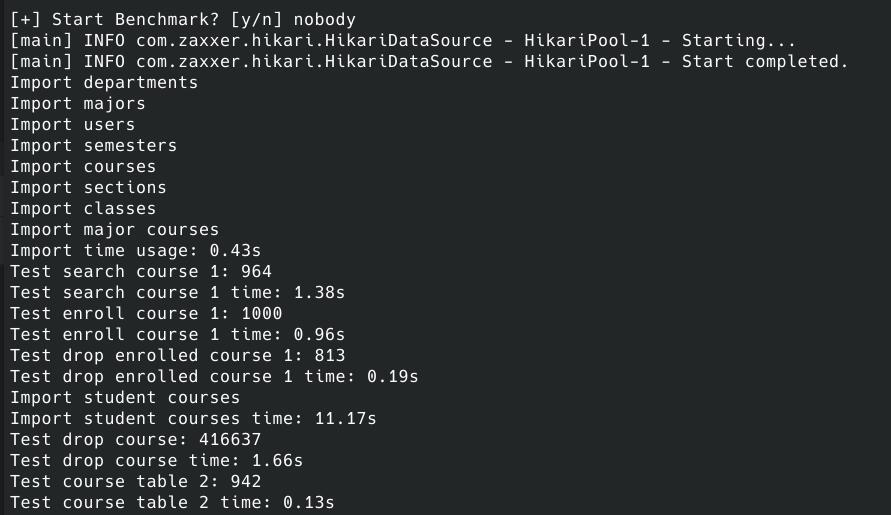
Speed and Correctness 优化:用流进行searchcourse筛选,但要注意的是一些情况不适用,只能进行for循环筛选。
其中,drop course 共有146637条命令,正确执行146637条,正确率为100%。
drop enrolled course共有 813 条命令,正确率为100%。
其余的test样例数为1000条,通过率在90%-100%之间。
Concurrency
在ProjectJudge文件中,每一个查询指令都是并行查询,例如在testCourseTables中:
1 2 3 List<CourseTable> courseTableResults = IntStream.range(0 , courseTableParams.size()).parallel() .mapToObj(it -> testCourseTable(courseTableParams.get(it))) .collect(Collectors.toUnmodifiableList());
其中,每次的查询总数大约有1000条。
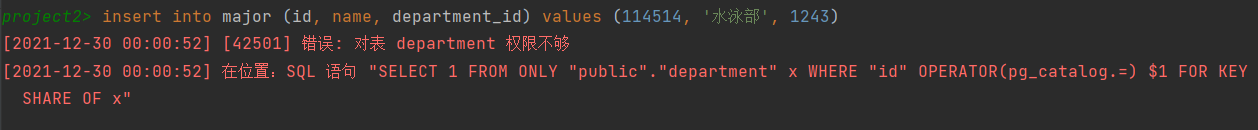
在这个数据库中,有且仅有一个user能够拥有改变表中信息的权限。只有在config中输入正确的username和password才能成功连接上数据库并查询或修改里面的数据。我们还创造了一个新的用户students,用来代表使用这个数据库的学生,他没有修改任何一个表的权限,但是可以查询表中的内容。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 create user students password '123456' ;alter database project2 owner to students;alter table course owner to students;alter table department owner to students;alter table instructor owner to students;alter table major owner to students;alter table major_course owner to students;alter table section owner to students;alter table section_class owner to students;alter table semester owner to students;alter table student owner to students;alter table student_section owner to students;revoke update on course from students;revoke update on department from students;revoke update on instructor from students;revoke update on major from students;revoke update on major_course from students;revoke update on section from students;revoke update on section_class from students;revoke update on semester from students;revoke update on student from students;revoke update on student_section from students;
所以,如果是以普通的student的身份是无法修改表中信息的。
特点 用流进行searchCourse()的筛选 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Stream<Info> infos = Util.query(Info.class, con, sql,semesterId).stream().parallel(); if (searchCid!=null && !searchCid.equals("" )){ infos=infos.filter(info -> info.courseId.contains(searchCid)); } if (searchName!=null && !searchName.equals("" )){ infos=infos.filter(info -> info.courseFullName.contains(searchName)); } if (ignoreFull){ infos=infos.filter(info -> info.leftCapacity>0 ); } List<Info> infoList = infos.collect(Collectors.toList()); HashSet<Integer> filteredSids = new HashSet <>(); for (Info info : infoList) { if ((searchInstructor==null ||searchInstructor.equals("" )||info.instructorFullName.replace(" " ,"" ).contains(searchInstructor.replace(" " ,"" )))&& (searchDayOfWeek==null ||info.dayOfWeek == searchDayOfWeek)&& (searchClassTime==null ||info.classBegin <= searchClassTime && info.classEnd >= searchClassTime) ){ if (searchClassLocations!=null && !searchClassLocations.isEmpty()){ for (String eachLocation : searchClassLocations) { if (info.location.contains(eachLocation)){ filteredSids.add(info.sectionId); break ; } } }else {filteredSids.add(info.sectionId);} } } infoList.removeIf(info -> !filteredSids.contains(info.sectionId));
用逆波兰算法处理先修课string 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 public boolean passedPre (ArrayList<String> passedCids,String courseId) { try (Connection con=SQLDataSource.getInstance().getSQLConnection()){ String sql="select prerequisite from course where id=?" ; String pre = (String)Util.querySingle(con, sql, courseId).get(0 ); if (pre==null ){return true ;} String[] preCids = pre.split(" (AND|OR) " ); for (int i = 0 ; i < preCids.length; i++) { preCids[i]=preCids[i].replaceAll("[()]" ,"" ); } pre=pre.replace(" AND " ,"&" ).replace(" OR " ,"|" ); for (String preCid : preCids) { pre=pre.replace(preCid,passedCids.contains(preCid)?"T" :"F" ); } Stack<Character> stack = new Stack <>(); StringBuilder postfix = new StringBuilder (); for (char c : pre.toCharArray()) { switch (c) { case '(' -> stack.push('(' ); case ')' -> { char top; while ((top = stack.pop()) != '(' ) { postfix.append(top); } } case '&' -> { if (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == '&' ) { postfix.append(stack.pop()); } stack.push('&' ); } case '|' -> { if (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == '&' ) { postfix.append(stack.pop()); } if (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == '|' ) { postfix.append(stack.pop()); } stack.push('|' ); } default -> postfix.append(c); } } while (!stack.isEmpty()){ postfix.append(stack.pop()); } Stack<Boolean> stack2 = new Stack <>(); for (char c : postfix.toString().toCharArray()) { switch (c){ case '|' -> stack2.push(stack2.pop() | stack2.pop()); case '&' -> stack2.push(stack2.pop() & stack2.pop()); case 'T' -> stack2.push(true ); case 'F' -> stack2.push(false ); } } return stack2.pop(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(1 ); return false ; } }
用synchonized解决updateLeftCapacity()的并发问题 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 private synchronized void updateLeftCapacity (Connection con,int sectionId,boolean isAdd) throws SQLException{ String addSql= """ update section set left_capacity=( select left_capacity from section where id=? )-1 where id=?""" ; String dropSql= """ update section set left_capacity=( select left_capacity from section where id=? )+1 where id=?""" ; PreparedStatement ps; if (isAdd){ps=con.prepareStatement(addSql);} else {ps=con.prepareStatement(dropSql);} ps.setInt(1 ,sectionId); ps.setInt(2 ,sectionId); ps.executeUpdate(); ps.close(); }
做project过程中的收获
本次项目中,我们小组为了方便合作及代码分工,每个组员都学习了Git的有关知识,并且在GitHub上创建了仓库,通过IDEA的Git集成,可以很方便的同步代码
在project1中,虽然我们也用到了JDBC的方式来连接并使用数据库,但仅仅局限于简单的数据插入和查找,格式固定,自动化程度低,无法满足大量不同数据同时插入、查找及更新。而在本次project中,逐个实现不同的service,不同的方法,让数据的增删改查都流程化,只需正确使用每一个service,就能很高效地向数据库中插入数据。
当很多不同的方法需要使用同样的增删改查操作时,我们学会了用Util类将这些多次使用的方法进行封装。能很大程度上提升代码的简洁性和易读性,并且能减少因为逻辑错误而产生bug的风险。